Getting started
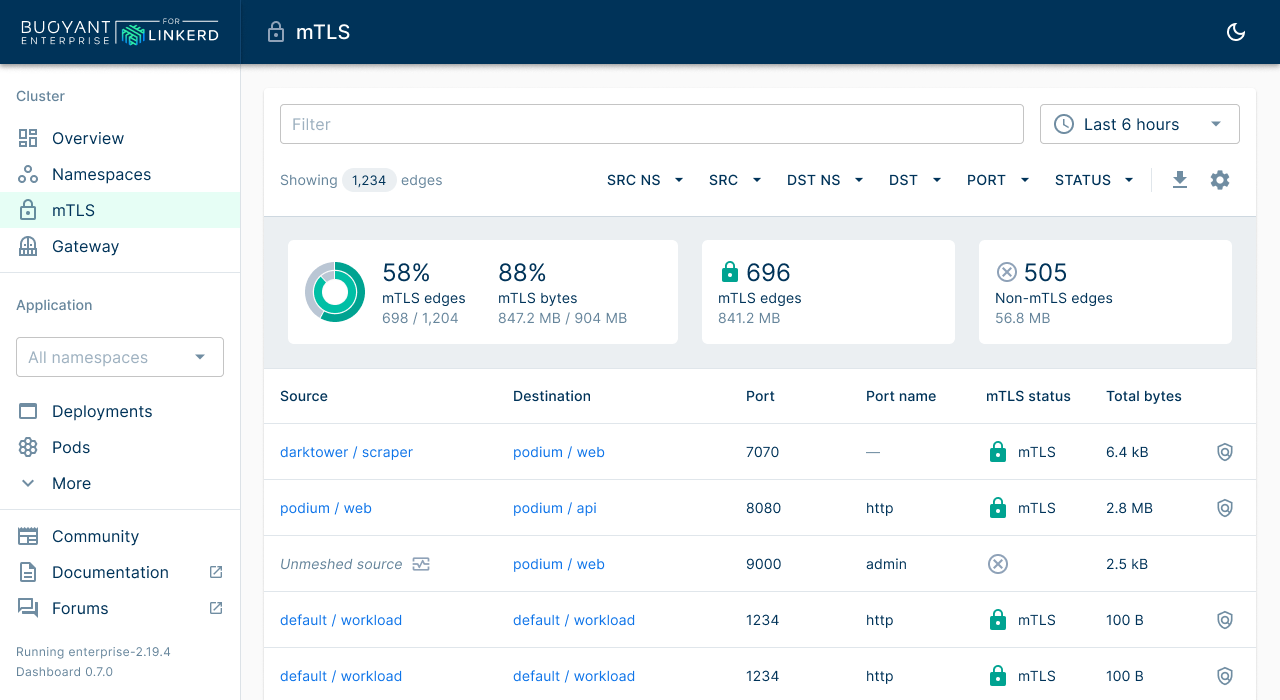
The Linkerd dashboard provides a user-friendly interface for monitoring and managing your Linkerd service mesh within a cluster.
With the dashboard, you can:
- Monitor the health of the Linkerd control plane.
- View key performance metrics (“golden metrics”) for all meshed workloads in your cluster.
- Visualize traffic flow between workloads with an interactive traffic chart, making it easy to identify issues within your service call chain.
Metrics pipeline
The Linkerd dashboard ships with a built-in Prometheus instance that is configured to scrape all Linkerd proxies on the cluster and to store that data for 6 hours.
Installation
The dashboard is managed via a Helm chart. To install or upgrade to the latest stable version, run:
helm upgrade -i -n monitoring --create-namespace \
linkerd-dashboard oci://ghcr.io/buoyantio/charts/linkerd-dashboard
--version flag.Accessing the dashboard
To access the dashboard, forward port 8080 from the dashboard workload:
kubectl -n monitoring port-forward deployments/linkerd-dashboard 8080 &
Then, open your browser and navigate to http://localhost:8080.
Configuring multi-cluster policy
If you have installed the
multi-cluster extension,
it includes a policy configuration that prevents unauthorized access to pods
running in the linkerd-multicluster namespace. This policy configuration only
grants access to the core Linkerd control plane by default. To see multi-cluster
metrics in the dashboard, you’ll need to add the following configuration to the
linkerd-multicluster namespace:
apiVersion: policy.linkerd.io/v1beta1
kind: ServerAuthorization
metadata:
annotations:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: linkerd-buoyant
name: service-mirror-linkerd-dashboard
namespace: linkerd-multicluster
spec:
client:
meshTLS:
serviceAccounts:
- name: linkerd-dashboard
namespace: monitoring
server:
name: service-mirror
If you save the above configuration as policy.yaml, you can apply it to your
cluster with:
kubectl apply -f policy.yaml
